Water-Powered Cars
Imagine a world where we power the cars we drive with water instead of fossil fuels. This revolutionary idea can change transportation as we know it. A future with water-powered vehicles could reduce pollution, conserve natural resources, and cut fuel costs dramatically. The concept has sparked curiosity for decades, but is it truly achievable?
Many debates have revolved around water-powered cars. The following are questions that arise from most of these discussions: "Are water-powered cars real?" "Why are water-powered cars not available yet?" This blog talks about the possibilities, problems, and realities behind such cars.
What Are Water-Powered Cars?
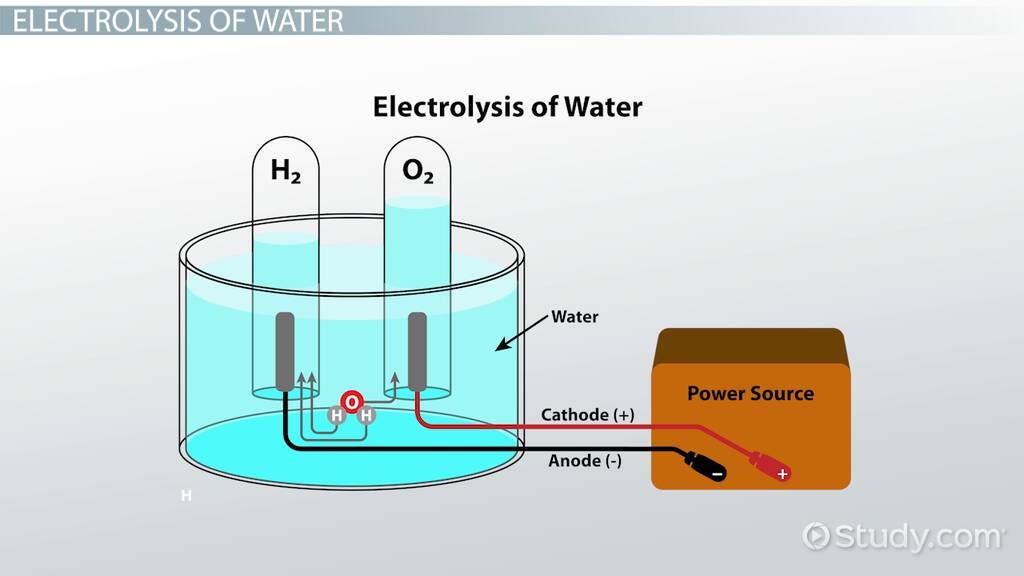
Water-powered cars are vehicles that use water as the primary source of energy. Instead of working like traditional gasoline- or diesel-powered engines, they extract hydrogen from water. Through a process called electrolysis, hydrogen is separated from water and then used as fuel.
This concept has piqued the interest of many inventors and automobile enthusiasts. Companies like Toyota have made significant investments in hydrogen fuel cell technology, exploring ways to incorporate it into modern vehicles. While people often refer to these cars as water-powered, the reality is more nuanced. They rely on hydrogen as the energy carrier rather than the water itself.
Who Invented Water-Powered Cars?
In the 1960s, Filipino inventor Daniel Dingel claimed to power a car solely using water. He is one of the notable pioneers behind the idea of running cars on water, along with a few other key figures. Not much was considered about his findings since there is no scientific basis to prove him right.
Stanley Meyer, an American inventor, became widely known in the 1980s for patenting a water fuel cell, which he claimed could power a car using water as a source of hydrogen fuel. His work and claims have since sparked both interest and controversy within the scientific community and among alternative energy enthusiasts. He believed that his invention was going to change the automobile industry, but many critics dismissed it as unproven. His sudden death in the late 1990s has fueled speculations and conspiracy theories about the suppression of water-powered technology.
How Do Water-Powered Cars Work?
Water-powered cars work on the principle of breaking water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen. The process of separating water into its basic components can be done using electrolysis by passing an electric current through it. The collected hydrogen can then be stored and fed into an engine or used in a fuel cell to generate electricity.
The concept is scientifically sound, but breaking hydrogen from water requires a significant amount of energy. Hydrogen is required to be produced on an industrial scale with a significant amount of energy, and the electricity used for this process is typically generated from non-renewable sources. As a result, it remains uncertain whether water-powered vehicles are truly environmentally friendly.
Are Cars Powered with Water Real?
The idea of cars powered solely by water is more theoretical than practical. The Toyota Mirai, a hydrogen fuel cell car, has become a symbol of green transport in recent years. However, it doesn't actually run on water; instead, it uses hydrogen derived from water as its fuel source, making it an indirect process.
Many car manufacturers, such as Toyota and BMW, have also developed hydrogen fuel cell technology. However, the infrastructure to produce and distribute hydrogen is still in its early stages, limiting widespread adoption.
Why Are There No Water-Powered Cars?
There are several reasons why water-powered cars are not yet available. The main issue is the inefficiency of the energy conversion process. Extracting hydrogen from water requires more energy than the hydrogen can provide, making it an impractical solution.
Another barrier is the infrastructure required for production and distribution, which demands significant investment and development. Until advancements are made in energy efficiency and the establishment of a robust infrastructure, water-powered vehicles will likely remain a concept rather than a reality. Hydrogen fueling requires the construction of facilities that are expensive and time-consuming to develop. The entire automotive industry faces resistance from stakeholders in fossil fuel technologies.
Technical complexities also pose a challenge. Hydrogen-powered engines or fuel cells involve highly complex engineering issues. These combined factors explain why water-powered cars remain an idea rather than a reality.
Advantages of Water-Powered Cars
If water-powered cars were possible, they would offer numerous advantages. A significant benefit would be the reduction of harmful emissions. Since the byproduct of hydrogen fuel cells is water vapor, these vehicles would produce no air pollution.
The reduction in travel costs could lead to increased disposable income, allowing consumers to allocate funds toward other essential needs or leisure activities. Additionally, it could encourage more people to embrace sustainable transportation options, further benefiting the environment. Water is readily available and inexpensive compared to fossil fuels, making water-powered technology a potentially affordable transportation solution in the future.
Water-powered cars could also help address climate change issues. Reducing dependence on fossil fuels would decrease the emission of greenhouse gases, slowing the rate of global warming.
Obstacles and Limitations
One significant hurdle is the development of efficient water electrolysis systems that can convert water into hydrogen fuel cost-effectively. The transition to water-powered vehicles faces challenges due to the current dominance of fossil fuels and the extensive existing infrastructure supporting them. Public skepticism and resistance to new technologies may also hinder the rapid adoption necessary for this innovation to flourish.
Producing hydrogen is energy-intensive. Extracting hydrogen through electrolysis requires significant electricity, usually sourced from fossil fuels, which reduces the environmental benefits of the technology.
Technical complexity is another challenge. Designing an engine or fuel cell for hydrogen-powered vehicles is highly technical. Engineers must solve numerous problems to create efficient and reliable systems.
Infrastructure remains a major challenge. Hydrogen requires dedicated production, storage, and transport facilities that are not currently available in abundance.
Role of Automakers
Automakers are developing alternatives to fossil fuels. Companies such as Toyota, BMW, and even Tesla have focused on hydrogen and electric car technology. For example, Toyota unveiled the Mirai, a hydrogen fuel cell car.
Elon Musk, known for his contributions to electric vehicles, has expressed skepticism about hydrogen-powered cars. His visionary ideas and commitment to sustainability have inspired a new generation of engineers and designers. As companies strive to adopt greener technologies, his legacy serves as a guiding light for future advancements.
Are Water-Powered Cars the Future?
Recent advancements in technology and research are paving the way for water as a viable fuel source. Scientists are exploring methods to efficiently harness hydrogen from water, potentially revolutionizing the automotive industry and reducing reliance on fossil fuels. With advancements in renewable energy and hydrogen production, water-powered cars could soon become a reality. Enhanced technology could improve hydrogen extraction efficiency and fuel cell design, making water-powered cars feasible.
For now, the focus is on reducing emissions and moving towards cleaner energy sources. Whether through hydrogen, electricity, or another innovative solution, the future of transportation looks promising.
Conclusion
Water-powered cars represent a fascinating vision of sustainable transportation. Although they are not yet a practical reality, the concept continues to inspire inventors, engineers, and environmentalists. Exploring alternatives to fossil fuels is crucial for a greener and cleaner future.
What are your thoughts on water-powered cars? Would you embrace this technology if it became widely available? Share your thoughts in the comments section below. Subscribe to our newsletter for more insights into innovative technologies and sustainable living.
Additional Topics and Content
Differences Between Hydrogen Cars and Water-Powered Cars
Though often referred to as water-powered, hydrogen cars are distinct in their energy source. The Toyota Mirai is a hydrogen fuel cell car that runs on hydrogen gas stored in tanks, while the concept of true water-powered cars would draw hydrogen from water. These two vehicle types present vastly different engineering and infrastructure challenges, making hydrogen cars the more practical option for now.
The History of Water-Powered Cars
The idea of using water as fuel has been discussed for decades. Pioneers like Daniel Dingel and Stanley Meyer claimed to have developed water-powered vehicles. Though their inventions were groundbreaking, they lacked the scientific and industrial support needed to scale the technology. Years later, the dream of water-powered cars continues to inspire inventors but remains elusive.
Are Water-Powered Cars Legal?
There is no direct legislation banning water-powered cars, but the lack of practical technology and standardization means they are not commercially available. Legality depends on safety standards, emissions testing, and regulations governing alternative fuels. Governments worldwide are promoting sustainable energy initiatives, which could eventually include water-based technologies.
Why Water-Powered Cars Could Save the Planet
This innovative approach not only reduces greenhouse gas emissions but also promotes sustainable practices. As technology advances, water-powered vehicles could significantly decrease our reliance on fossil fuels. Water, covering 70% of the planet, is an easily accessible resource that could democratize energy access, decrease dependence on oil-rich regions, and increase global energy equality.
Frequently Asked Questions About Water-Powered Cars
1. Are water-powered cars real?
In the truest sense, water-powered cars do not exist today. Hydrogen fuel cell vehicles may use hydrogen derived from water, but they are not powered by water itself.
2. Who discovered water-powered cars?
Several inventors, including Daniel Dingel and Stanley Meyer, claimed to have invented water-powered cars. Their inventions remain surrounded by controversy and skepticism.
3. Why don't we have water-powered cars?
The main limitation is the technically challenging process of extracting hydrogen from water, which is inefficient and comes with high energy costs. The necessary infrastructure is also lacking.
4. Are water-powered cars illegal?
No, water-powered cars are not illegal. However, they must meet regulatory standards and safety requirements, which is challenging given the unproven technology.
5. How do water-powered cars work?
These cars theoretically work by splitting water into hydrogen and oxygen through electrolysis. The hydrogen is then used as fuel to power an engine or generate electricity in a fuel cell.
6. Are water-powered cars efficient?
Water-powered cars have significant efficiency problems. It typically requires more energy to extract hydrogen than it produces, making it inefficient.
7. Why are there no water-powered cars on the market?
There are many reasons, including expensive technology, lack of infrastructure, and inefficient methods of producing hydrogen.
8. Can water power an automobile?
Theoretically, water can power an automobile through hydrogen extraction, though this process is complex and energy-intensive in its current form.
9. Are hydrogen automobiles powered by water?
Hydrogen cars use hydrogen gas derived from water. They are not directly powered by water but depend on it as a hydrogen source.
10. Will water-powered cars be the future?
While water-powered cars are currently just an idea, ongoing research in hydrogen technology and renewable energy could make them a reality in the future.
If you find any mistakes or would like to request the removal of images, please contact us. We will review and make the necessary changes within 48 hours. Thank you for your understanding!












0 Comments